Configuring interfaces for Master Engines
Master Engines can have two types of interfaces: interfaces for the Master Engine's own traffic, and interfaces that are used by the Virtual Engines hosted on the Master Engine.
You can add Physical Interfaces and VLAN Interfaces to a Master Engine. If you want to use a Physical Interface or VLAN Interface to host a Virtual Engine, you must select a Virtual Resource for the interface. The same Virtual Resource can be used on more than one Master Engine interface to allocate multiple interfaces to the same Virtual Engine. If you want the Virtual Engine to have multiple interfaces, you must use the same Virtual Resource on more than one Master Engine interface.
If you want to use a Physical Interface or VLAN Interface for the Master Engine’s system communications, you can add IP addresses to either:
- An interface that does not have a Virtual Resource assigned to it
- A shared interface that has Virtual Resources assigned to it
By default, the Physical Interface definitions for the Master Engine are mapped to the actual network interfaces on the Master Engine hardware in numerical order. If necessary, you can change the mapping using command-line tools on the Master Engine. This mapping can be done differently from one Master Engine node to another. Make sure that the interface that represents the same network interface on each Master Engine node is correctly cabled to the same network.
Shared interfaces
A shared interface is a single layer 3 physical interface on the Master Engine in the Engine/VPN role. You can assign multiple Virtual Resources to the interface, so the interface can be shared by multiple Virtual Engines. The shared interface can also have shared VLANs underneath it.
Aggregated interfaces
To use an aggregated interface as an interface for a Virtual Engine, you must do one of the following:
- Make the aggregate interface a shared interface.
- Make the aggregate interface a shared interface, add shared VLAN interfaces to the interface, then assign the Virtual Resources to the shared VLAN interfaces.
- Add VLAN interfaces to a regular aggregate interface, then assign the Virtual Resources to the VLAN interfaces.
Interface examples
Figure: Example of Master Engine and Virtual Engines
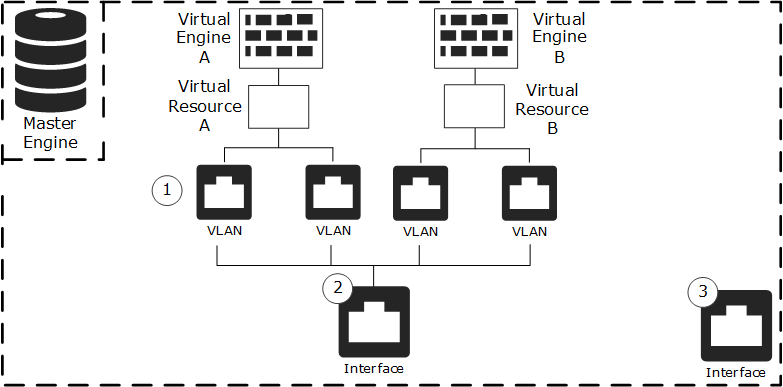
- 1
- VLAN Interfaces for hosted Virtual Engine traffic.
- 2
- Physical Interface for hosted Virtual Engine traffic.
- 3
- Physical Interface for the Master Engine system communications.
Figure: Example of shared interface on a Master Engine and Virtual Engines
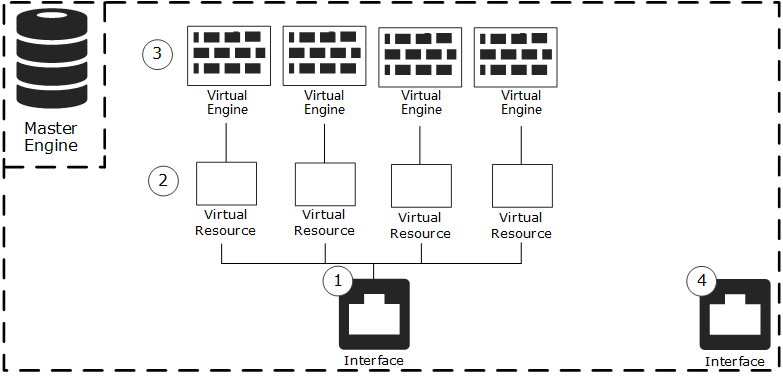
- 1
- Shared physical interface for hosted Virtual Engine traffic.
- 2
- Virtual Resources selected for the shared physical interface.
- 2
- Virtual Engines associated with the Virtual Resources.
- 4
- Physical Interface for the Master Engine system communications.
Figure: Example of Master Engine and Virtual IPS engines
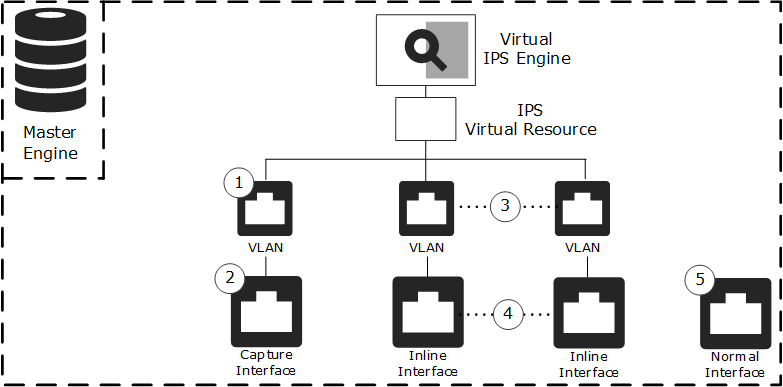
- 1
- VLAN Interface for hosted Virtual IPS engine traffic.
- 2
- Capture Interface for hosted Virtual IPS engine traffic.
- 3
- Inline VLAN Interface pair for hosted Virtual IPS engine traffic.
- 4
- Inline Interface pair for hosted Virtual IPS engine traffic.
- 5
- Physical Interface for the Master Engine system communications.
Figure: Example of Master Engine and Virtual Layer 2 Engine
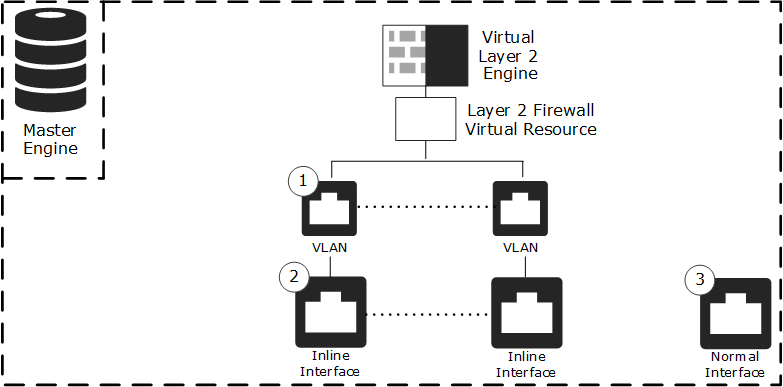
- 1
- Inline VLAN Interface for hosted Virtual Layer 2 Engine traffic.
- 2
- Inline Interface for hosted Virtual Layer 2 Engine traffic.
- 3
- Physical Interface for the Master Engine system communications.