Block listing process
Block listing is executed as defined in the Access rules. Automatic block listing requests are sent as defined in the Inspection Policy.
Figure: Block listing process
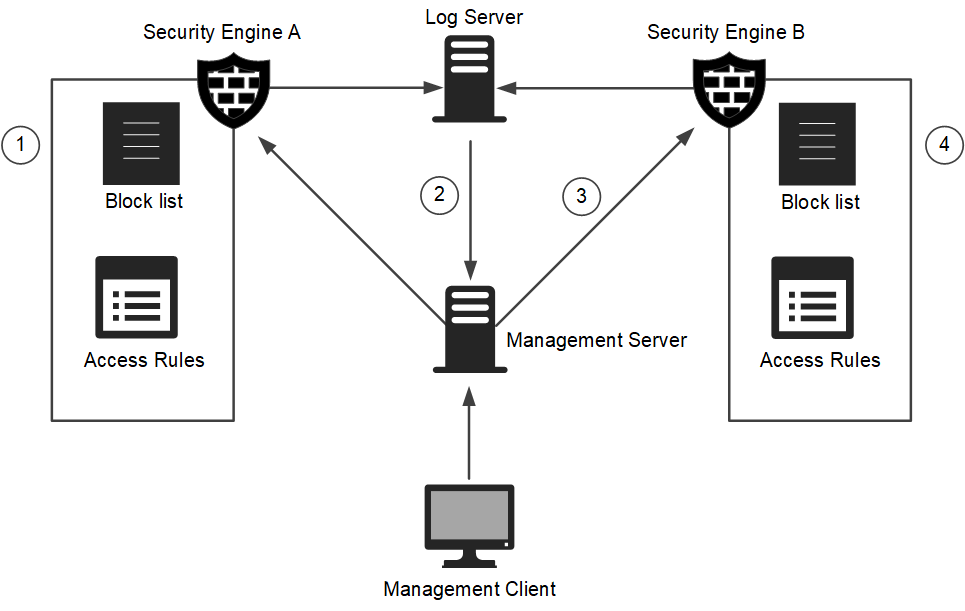
- 1
- Engines add entries to their own block lists for traffic they inspect.
- There is one block list for each Engine, Layer 2 Engine, IPS engine, or Virtual Engine.
- In engine clusters, there is one block list for each cluster. The nodes in the cluster exchange block list information in their synchronization communications.
- 2
- Log Servers send block listing requests as a response to correlation of detected events. When one Secure SD-WAN Engine sends a block listing request to another Secure SD-WAN Engine, the Log Server relays the block listing request to the Management Server.
- 3
- Management Servers relay manual block listing commands from administrators, and block listing requests sent by Log Servers to the Secure SD-WAN
Engines.
There is no direct communication between different Virtual Engines or between Virtual Secure SD-WAN Engines and the Management Server. For this reason, Virtual Engines cannot send block listing requests to other Virtual Engines.
- 4
- Engines enforce the entries on their block lists according to their Access rules.
- Each block list entry exists only for a defined duration, after which the entry is removed from the block list, and matching connections are again allowed. The duration of the blocking is defined when the block list entry is created.
- Access rules check connections against the block list. If the IP addresses and ports in one of the block list entries match, the connection is discarded.
- If the connection does not match a block listing Access rule or its related block list entries, the next Access rule in the policy is checked as usual.