In policy-based VPNs, you can redirect traffic from one VPN tunnel to another VPN tunnel through a hub gateway.
Before you begin
You must have a policy-based VPN configured. If VPN client traffic is forwarded, you must configure virtual IP addressing for VPN clients.
Redirecting traffic between VPN tunnels is especially useful for VPN client users who need access to resources at different locations. When you redirect traffic between VPN tunnels, users do not
have to separately connect to different gateways.
 For more details about the product and how to configure features, click Help or
press F1.
For more details about the product and how to configure features, click Help or
press F1.
Steps
-
Select
 Configuration, then browse to Secure SD-WAN.
Configuration, then browse to Secure SD-WAN.
-
Browse to Policy-Based SD-WANs.
-
Right-click the Policy-Based SD-WAN element, then select Edit <element name>.
-
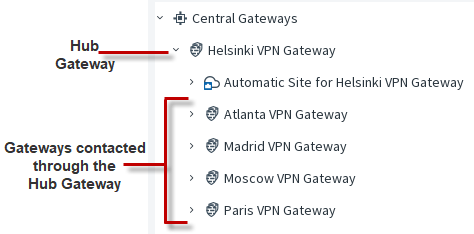
On the Site-to-Site SD-WAN tab of the Policy-Based SD-WAN editing view, place the forwarding hub gateway at the top level of the
Central Gateways list.
-
Place the gateways that are contacted through the hub under the hub gateway.
Note: Duplicate tunnels are not allowed. There must not be site-to-site connections between the hub and the other gateways in other active VPNs.
-
Add a Site element that contains the IP addresses behind the spoke gateways under the hub gateway.
-
Set the
Mode of the Site element to
Hub.
-
Disable the Site element in any other VPNs where it is used.
The protected IP addresses are behind the spoke gateways.
-
To forward VPN client traffic, add a Site element that contains the virtual IP address space used for the VPN clients under the hub gateway.
-
Add Access rules that forward the traffic between tunnels.
-
Refresh the policies of all engines involved in the VPN, starting from the engine that acts as the hub gateway.
Optionally, all traffic (including Internet traffic) can be routed through the hub gateway.
For more details about the product and how to configure features, click Help or
press F1.