Configuring Microsoft Information Protection
Use the Microsoft Information Protection Properties page to decrypt and analyze Microsoft Office files encrypted by Microsoft Information Protection (MIP), to import Microsoft Information Protection labels for detection (for more information about creating file labeling classifiers for detection, see File Labeling section), and for labeling (for more information about configuring labels in an action plan, see Forcepoint Data Discovery options section).
To open the Microsoft Information Protection Properties page, follow the instructions below:
- Navigate to tab.
- click the Microsoft Information Protection link.
The Microsoft Information Protection Properties page opens.
Microsoft Information Protection (MIP) can be used to protect files created using Office 2007 or later.
- Decrypt and analyze content that was encrypted using MIP.
- Detect and label content that was using MIP labels.
Microsoft admin Credentials
- Select type of the credentials from Credentials type drop-down.
The Credentials type drop-down has the below options:
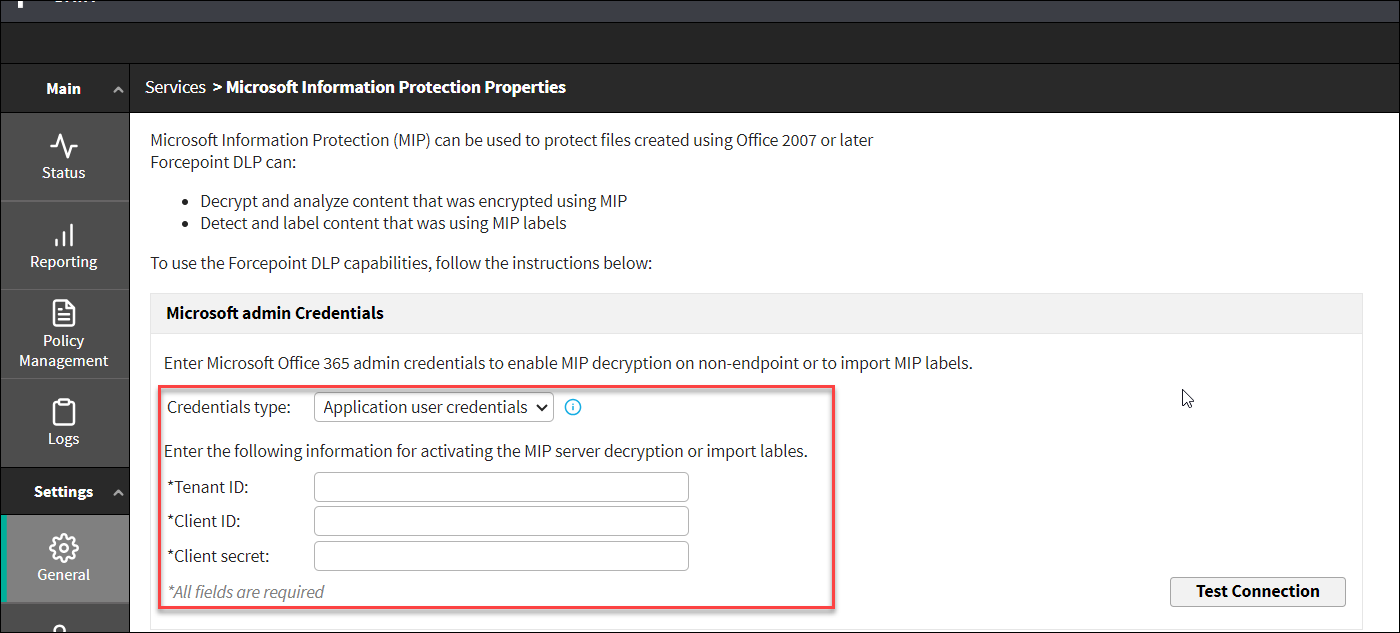
- Application credentials - This option is used for MIP decryption on non-endpoint channels or for importing MIP labels.
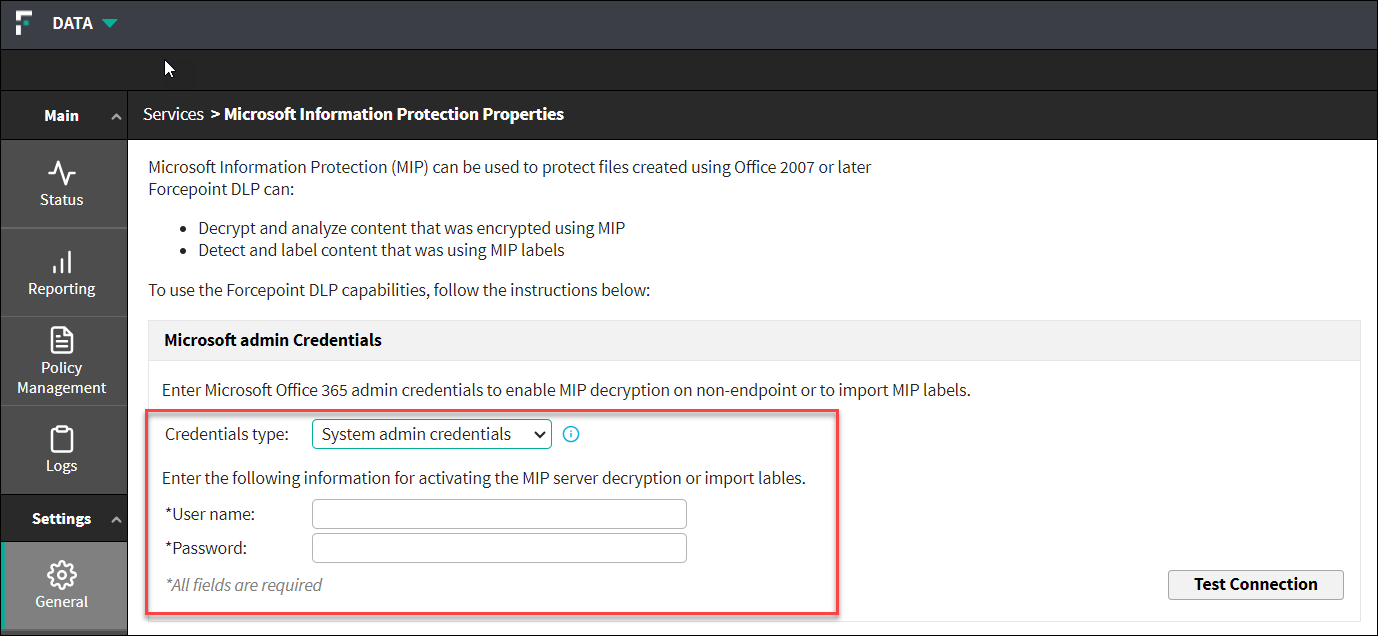
- System admin credentials - This option is used for importing MIP labels only. This information is not stored on the Forcepoint servers.
Note: MIP decryption on endpoints does not need credentials to work. - If you select Application credentials, follow the instructions
below:
- Enter the following information for activating the MIP server
decryption or import lables.
- Tenant ID
- Client ID
- Client secret
- Enter the following information for activating the MIP server
decryption or import lables.
- If you select System admin credentials, follow the instructions
below:
- Enter the following information for activating the MIP server
decryption or import lables.
- User name
- Password
- Enter the following information for activating the MIP server
decryption or import lables.
- Click Test Connection to test the connection.
If the connection fails, verify the credentials you entered.
MIP decryption
- Enable MIP decryption on endpoint channels:
Forcepoint DLP integrates with Microsoft Information Protection (MIP) to apply DLP policies to MIP-encrypted files on Windows endpoints. This feature enables enterprises to maintain sensitive data visibility and control for files protected using MIP. Forcepoint DLP interacts directly with MIP, enabling MIP to work both on and off the network. It can also be used to better understand how MIP is being used by employees to protect sensitive data.
Use the Enable MIP decryption on endpoint channels option to configure Forcepoint DLP to decrypt and analyze Microsoft Office files that were encrypted by Microsoft Information Protection on Windows endpoints. This includes files found on Windows endpoints (discovery) or sent via any endpoint channel.
Note: The MIP decryption feature relies on the Microsoft RDS SDK. Therefore, for MIP decryption to work, Microsoft Remote Desktop Services must be running on the endpoints.Office files that are protected by Microsoft Information Protection include Office File Formats based on OCP (Office 2010 and later), legacy Office File Formats (Office 2007), PDF files, Generic PFILE support, and files that support Adobe XMP.
The system uses logged-in user credentials to access the MIP server. As the system runs under the security context of the logged-in user, it uses the same permissions as the user has, and, therefore, can read everything that allows the user to read. For example, when a user creates a document, the user gets the permission to read the document and so does the system. When the user has read permissions to the document, explicitly or as part of an Active Directory group, so does the system. In case of any errors, the transaction is permitted without analysis and the error is recorded in a log file.
The Microsoft Information Protection file detection feature has the following prerequisites:- The endpoint machine must be in your organization’s domain.
- Forcepoint DLP Endpoint version 19.xx or higher must be installed.
- Azure Active Directory/Office 365 single sign-on (SSO) between the local active directory and the Azure active directory must be configured and working. Users must be able to MIP-decrypt a document without a login request.
To view MIP-related incidents in the Data Security module of the Forcepoint Security Manager, navigate to the page Main > Reporting > DLP > Incidents - Last 3 days.
See Microsoft documentation for more information on MIP:Note: Please note that the following are not supported:- Decryption of MIP-encrypted file can only be done for single logged-in user. Multiple users logged into the same machine is not supported.
- RPMSG message (RMS protected mail message) are not supported
- Enable MIP decryption on non-endpoint channels
Forcepoint DLP integrates with Microsoft Information Protection (MIP) to apply DLP policies to MIP-encrypted files on the following non-endpoint channels:
- Windows servers for network discovery channel
- Protectors certified upon Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, for both Network Email and Network Web channels (coming soon, stay tuned for further announcements regarding general availability).
- Data Protection Service for the following channels (stay tuned
for further announcements regarding general availability):
- Cloud web (by Forcepoint ONE SWG or Forcepoint Web Security Cloud)
- Cloud email (by Forcepoint Email Security Cloud)
- Cloud Proxy and Cloud API (by Forcepoint ONE CASB)
Import Labels:
Imported labels are used for detection by creating File Labeling classifiers and using them in rules and action plans.
- Before you import Microsoft Information Protection labels for the first
time, you must obtain permission for the Forcepoint application to import
the labels.
Log into the Microsoft 365 Admin Consent page, authenticate using your Microsoft 365 admin credentials, and accept the permissions statement.
- Forcepoint Security Manager enables import of sensitivity labels from the Microsoft 365 Security and Compliance Center. If you want to import Azure Information Protection labels, you must migrate them to Microsoft 365, as described on Microsoft’s Azure Information Protection site.
- Files that are protected by Microsoft Information Protection can be decrypted automatically during DLP analysis.
- For Microsoft 365 Admin Consent Prompt Permissions for Forcepoint DLP AIP Integration, see this article
- Enter your Microsoft Office 365 admin credentials and click Import
Labels.
We recommend that you enter credentials for an administrator who has visibility to all Microsoft Information Protection labels used in the organization.
User credentials are not stored on Forcepoint servers. However, you should ensure that your web browser does not store this information.
- Click OK to start the import process.
If “admin consent” has not already been established, this step generates an error message and the import does not occur. Complete the Microsoft admin consent process and try again.
- After a successful import, the Last Import Details section is updated with the imported labels and a message. The message lists date, time and number of imported labels.
File Labeling
To apply labels, mark the Apply file labels check box, and Click OK to save the changes.
When you enable the check box, you can define DLP action plans that use Microsoft Information Protection file labels.
The audit log () is updated when the administrator imports classification labels and when Apply file labels is either checked or unchecked.
After the Apply file labels check box has been marked, administrators can configure the specific labels to use on the Discovery tab of each action plan. See Action Plans section.
If any action plans include labels that no longer exist in the labeling system, a warning is displayed, with a Show details link, leading to a list of action plans with labels that are no longer in the labeling system. Forcepoint recommends updating these action plans. See Forcepoint Data Discovery options section.