Introduction to Forcepoint IPsec Advanced
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is an extension to the IP protocol that provides secure traffic tunneling by authenticating and encrypting information sent over a network. The IPsec protocol uses Internet Key Exchange (IKE) to establish session keys for encryption and decryption, and Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) to provide data confidentiality and integrity. Traffic to the Forcepoint IPsec Advanced service can be fully encapsulated in tunnel mode, providing complete traffic encryption.
Forcepoint IPsec Advanced supports transparent end user identification via NTLM, allowing users to browse the Internet without explicitly providing logon credentials. Typical uses for the IPsec
Advanced service include providing Forcepoint Web Security Cloud protection for:
- Remote offices
- Guest Wi-Fi networks
- Organizations that want to secure traffic sent to the cloud service
- Organizations that have dynamic egress IPs
- Organizations that do not want a Group Policy Object (GPO) or browser configuration
- Organizations that are unable to or do not want to install an endpoint on client machines
- Organizations with a “bring your own device” policy.
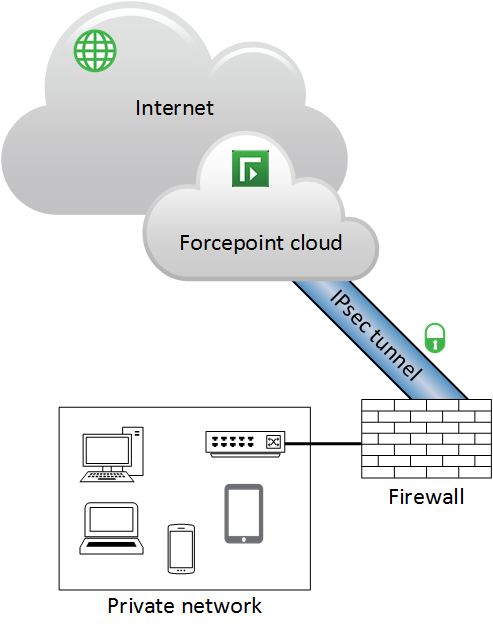
A typical site-to-site IPsec tunneling deployment is shown in the following diagram.
Benefits
Using IPsec Advanced to forward traffic to the cloud service can provide a number of benefits. These include:
- There is no need to install endpoint software on client machines or deploy browser configuration PAC files through Group Policy Objects - ideal for BYOD or guest networks.
- Traffic inside the tunnel can be protected via encryption
- Your network’s internal IP addresses are available to the cloud service, so:
- Policies can be created based on internal IP addresses, address ranges, or subnets
- Authentication bypass can be set based on IP addresses, address ranges, or subnets
- Reports can be created using internal IP addresses to identify individual users.