Set up end-user authentication
End-user authentication is driven by the setting configured in your Web policy. For IPsec Advanced traffic, the cloud service can perform either NTLM identification or manual authentication. NTLM identification uses the credentials presented by a user’s browser, and compares these to the user details you have synchronized with the cloud service in order to identify the user. Manual authentication requires users to log on before they can browse, using the email address and password registered with the cloud service.
The following graphic shows the Access Control tab in the cloud portal, used to define your authentication settings.
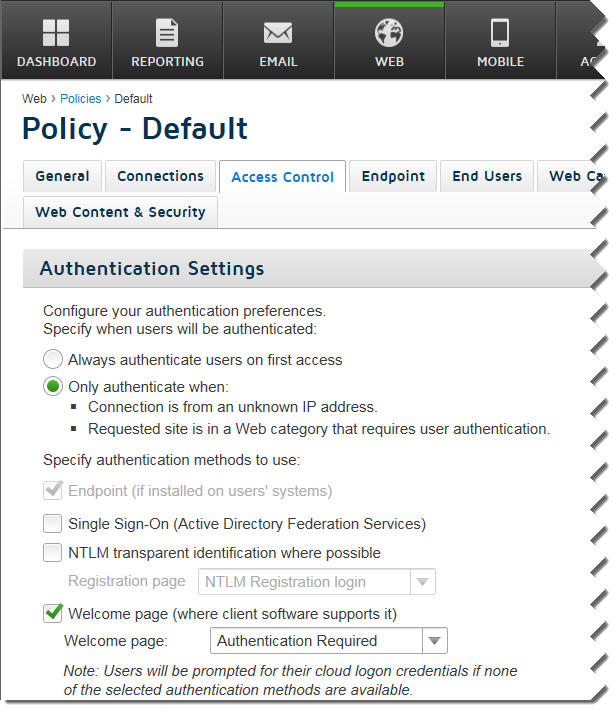
By default, manual authentication is enabled. If the Always authenticate users on first access option is set, users are prompted to authenticate when first logging on.
If NTLM identification is enabled, it is given priority and will be used instead of manual authentication. In order for NTLM identification to work seamlessly, you must synchronize end user information including NTLM IDs with the cloud service. (See Forcepoint Security Portal Help - Directory Synchronization). If a user cannot be identified via NTLM, the service defaults to manual authentication.
Authentication bypass
Both cloud and hybrid administrators can elect to bypass authentication based on internal IP addresses, ranges, or subnets. Forcepoint Technical Support must enable the Internal Bypass Rules for Edge Devices feature for your account. See Forcepoint Web Security Cloud Help - Bypassing authentication settings for more information.