Configuring Forcepoint Mobile
Configure Forcepoint Mobile settings using the Forcepoint ONE SSE portal. This section describes the configuration parameters available for Forcepoint Mobile.
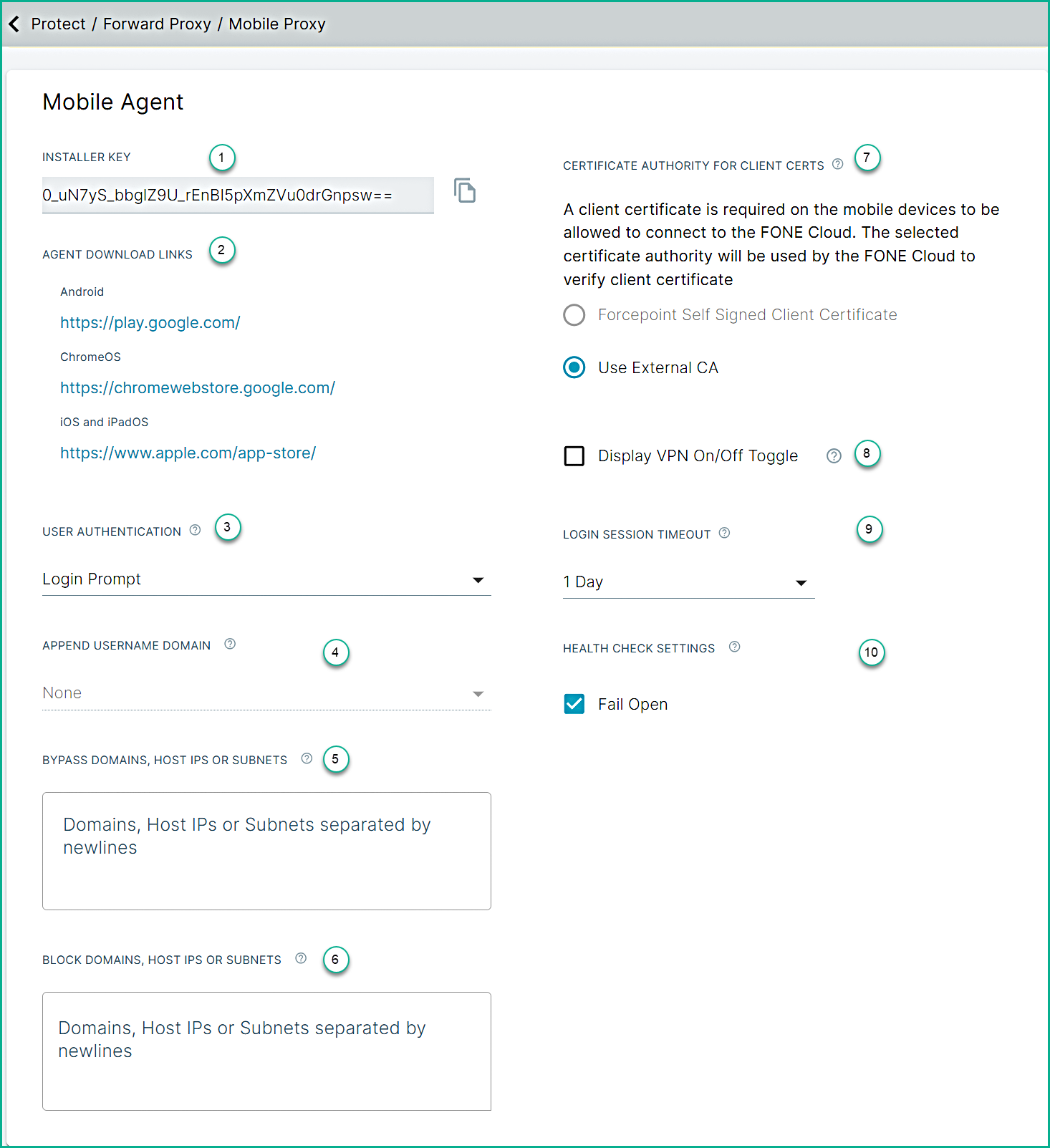
After logging into the Forcepoint ONE SSE portal, navigate to page to configure the settings. Administrators should set the settings before deploying the Forcepoint Mobile application.
This page includes the following sections:
- 1
- Download Mobile Config File: The Mobile Config File includes customer-specific information necessary for identifying the Tenant and various system details. It also includes an Installer Key and a payload certificate required for operation.
- 2
- Agent Download Links: Use the provided links to deploy the application via MDM on devices running the following operating systems (OS):
- Note: The links will be updated in a future release.Android
- Note: The links will be updated in a future release.ChromeOS
- iOS and iPadOS
- 3
- User Authentication: The admin can use the following authentication options to control how users are prompted to log in to the solution in order to apply policy controls.
- If the Login Prompt authentication is selected, the solution will display a web UI login prompt in the mobile application. The system shall use the standard login method for authentication.
- If the User Certificate authentication is selected, the solution will send the MDM-installed user certificate to the system. The system will then extract the
identifier (found after "CN=") from the certificate to be used to identify the user for login purposes. To successfully identify the user, the certificate must either insert the full
User Principle Name (UPN) after the common name identifier or insert a username string so that the system can append the username domain to obtain a full email
address or use an emailAddress field. For more information, see the following examples:
- Example 1: When the user certificate has a CN with an emailAddress field.
- Issuer: C=US, ST=California, L=Campbell, O=Bitglass, OU=SSE, CN=user1, emailAddress=user1@mobileagent.com
- The UPN is "user1@mobileagent.com"
- Example 2: When the user certificate has a CN with no domain.
- Issuer: C=US, ST=CA, O=FPONE, OU=FPONE, CN=user2
- User ID is "user2", then the full UPN is a combination of the User ID and the domain. Given a domain of XYZ.com.
- The UPN is "user2@xyz.com".Note: The CN does not have to be limited to just 6 characters.
- Example 3: When the user certificate has CN with a complete UPN.
- Issuer: C=US, ST=CA, O=FPONE, OU=FPONE, CN=user3@completeupn.com
- The full UPN is "user3@completeupn.com".
To learn more about append username domain, see the Append Username Domain section below.
- Example 1: When the user certificate has a CN with an emailAddress field.
- If the Anonymous authentication is selected, the solution will not prompt the user to login. Instead, the system will map all users to the anonymous user for policy. For this the Group field under the page must be set to Any.
- If the User Certificate, Login Prompt authentication is selected, the solution will attempt to log in to the user automatically using the User Certificate method described above. If that fails, it will present a Login Prompt.
- If the User Certificate, Anonymous authentication is selected, the solution will attempt to log in the user automatically using the User Certificate method described above. If that fails, it will default to Anonymous authentication.
After deploying the solution, the admin can modify the User Authentication setting if necessary. Changing the authentication mode will trigger automatic re-registration of all devices with the system. Any adjustments to these settings will log out all users, requiring them to log back into the system using the new authentication method.Note: It is advisable to update the authentication method during off-hours, as the devices will remain offline until they are re-registered. - 4
- Append Username Domain: This section is used for User Certificate authentication and requires a user certificate containing a
Common Name field. The domain selected here will be appended to the Common Name field from the certificate to obtain the UPN used to identify
the user for login purposes.
If the Common Name field in the user certificate contains the full UPN, select None. If automatic login is not desired, select None.
To learn more about user certificate authentication, see the User Certificate section above.
- 5
- Bypass Domains, Host IPS, or Subnets: List the domains or host IP addresses that should be bypassed by the solution on the device.
Example: If xyz.com needs to be bypassed, the solution will redirect the traffic straight to the Internet instead of to the Forcepoint ONE Cloud.
Add the domains or host IP addresses, one entry per line.
Note: Certificate pinned solutions should be bypassed for proper operation.Admins can add domains, host IPs, or subnets to the bypass list using wildcards. For example, you can use *.abc.net to bypass all subdomains of abc.net or specify a particular fully qualified domain name (FQDN) within that domain.
Moreover, you can bypass specific subsets of domains by utilizing wildcards. For example, the entry myabc*.stage.abc.net will include both myabc1.stage.abc.net and myabc2.stage.abc.net in the bypass list while excluding stuff.stage.abc.net.
The bypass list can include all of the following wildcards scenarios:- *.abc.com
- *foo.abc.com
- f*o.abc.com
- foo*.abc.com
- 6
- Corporate Networks for Mobile Bypass: List the URLs that can be used to ping and identify corporate networks. When connected to these networks, the device will
bypass the mobile VPN.Note:
- Add the URLs, one entry per line.
- This list will be used by the mobile app only.
Example: If the corporate network addresses are otherURL.companyname.com and pingURL.companyname.com, the list should contain:- 10.1.1.1
- pingURL.companyname.com
- 7
- DNS Bypass List: List the domains or IP addresses that bypass DNS servers. Also, include the corporate networks for the mobile bypass list.
Define the DNS server IP addresses using an escape prefix DNS. followed by the IP address. The application will then bypass these DNS server IP addresses.
Note: Add the domains or host IP addresses, one entry per line.Example: If the DNS servers are 8.1.2.3 and 182.7.8.9, and a corporate network pingURL.companyname.com, the list should contain:- 8.1.2.3
- 182.7.8.9
- pingURL.companyname.com
- 8
- Certificate Authority for Client certs: Select a certificate authority to verify client certificates for the Forcepoint ONE
cloud. A client certificate is required on mobile devices to be allowed to connect to the Forcepoint ONE cloud.
- Note: The following feature will be available in future releases.Forcepoint Self Signed Client Certificate
- Use External CA
- 9
- Display VPN On/Off Toggle: Allow the admin to configure an on/off toggle button for the solution.
- If the box is checked: The solution will display an On/Off toggle button that allows the user to turn the inspection service on or off.
- When the user selects On, the VPN activates, and the solution will inspect all network traffic. This means the device will use the configuration from the server to decide whether to proxy or send the traffic directly to the internet.
- When the user selects Off, the solution will bypass all traffic directly to the internet.
- If the box is unchecked: the mobile solution will not display this toggle button, and all traffic will be subject to solution inspection.
For more details, see the Using Forcepoint Mobile application page.
- If the box is checked: The solution will display an On/Off toggle button that allows the user to turn the inspection service on or off.
- 10
- Login Session Timeout: Configure the period after which the user login credentials are re-validated.
- 11
- Health Check Settings:
- If Fail Open box is checked: The solution will send traffic directly to the internet when the Forcepoint ONE cloud service is down.
- If Fail Open box is unchecked: The solution will block web traffic when the Forcepoint ONE cloud service is unavailable.
Note: The web traffic will be blocked if the user is not logged in, regardless of these settings.