Troubleshooting error pages for private application access
The following are some suggested steps to troubleshoot some common error conditions, and some error and block pages you might encounter.
If you need further assistance after following these troubleshooting tips, raise a case with Forcepoint Technical Support.
| Block or error page | Meaning | What to check |
|---|---|---|
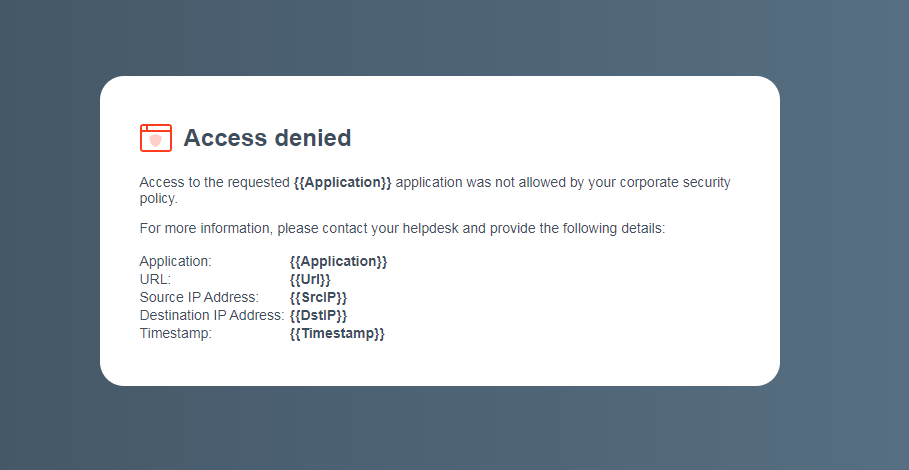
| Access denied page | An Access denied page can be displayed in cases where the request is successfully routed to the Private Access service, but access is prevented for one of the following reasons:
|
Check that your private application is configured correctly in the Private Access portal. Check that you have an Allow policy rule for the private application with your user assigned to the rule. Check that the user is provisioned to the Private Access user directory. Allow up to 35 minutes after provisioning a user or moving the user between groups before testing access for that user. Ensure you have deployed changes within the Private Access portal, and waited five minutes for the changes to take effect. Check your identity provider/single sign-on integration. |
| Authentication failure page | An Authentication failure page can be displayed if the request is routed to the service edge but cannot be processed for one of the following reasons:
 |
Check that you have installed a supported version of endpoint. Check that you have installed endpoint using the correct WSCONTEXT/account token for your account.
Tip: To check the account token that has been used for the endpoint install on a Windows machine, you can search "InitContext" in the Windows registry using
regedit. If you have installed a supported version of endpoint using the correct account token, contact Forcepoint support. Check that the PAC file has entries for the application's External FQDN and the Service edge address associated with your hosting site. Check that these settings match those configured for the private application on the page. If the PAC file does not contain the correct entries:
Using Chrome Developer Tools or similar, generate a .HAR (HTTP Archive) file for your request to the private application, to check that the request is being routed to the correct location. This file can also be provided to Forcepoint support to assist with troubleshooting. |
| Service unavailable page | A Service unavailable page can be displayed if the request is routed to the service successfully but the service cannot access the internal application. 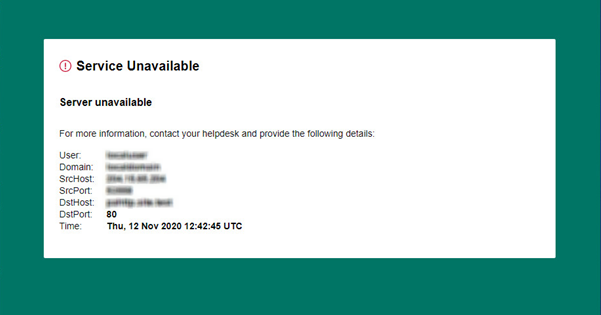 |
Ensure your private application definition is configured with the correct internal IP address in the Private Access portal. Ensure your tunnels are configured as active-active and always on. Requests to your private applications can come from either connection, and must be routed back to the same connection. Check that both IPsec tunnels to the service are up. Private Access performs network address translation (NAT) on incoming requests from users and presents a connection-specific source IP address. Your edge device must be configured to allow traffic from these IP addresses and route traffic back to the same address. Check that you have an access rule to allow requests to and from the Forcepoint Private Access addresses. Update your router to use the correct NAT addresses for the Private Access service:
Ensure your internal application is listening on the correct port. If possible, update your application to use port 80 or 443. Update the settings for your application in the Private Access portal to use port 80 or 443. |
| Cannot connect page | If you are using Private Access with Cloud Security Gateway, a Cannot connect page can be
displayed if you do not have proxy bypass entries in your PAC file to direct private application traffic to the service edge. |
Check that the endpoint is using the correct PAC file. To check the PAC file in use:
The endpoint should use the default PAC file address given on the page in the Cloud Security Gateway portal. Check that the PAC file has entries for the Service edge address associated with your hosting site. If the PAC file does not contain the correct entries, check the Proxy Bypass entry for the application on the page in the Cloud Security Gateway portal. |
| Browser timeout error | A browser timeout error such as "This site cannot be reached" can be displayed in the following cases:
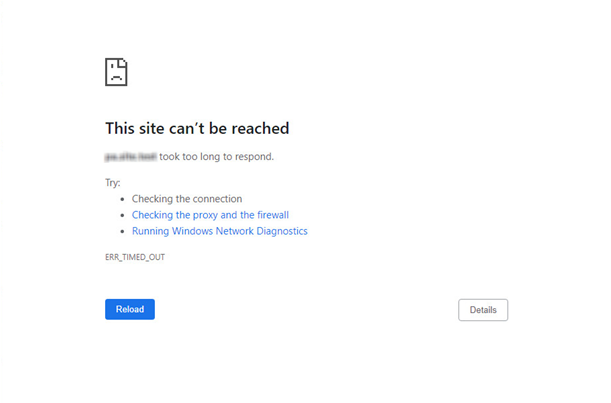 |
Private Access application policy settings. Remove any Block rules that are not followed by an Allow rule. All requests that do not match another rule are blocked by the default rule. Check that the endpoint is using the correct PAC file. To check the PAC file in use:
For Cloud Security Gateway users, endpoint should use the default PAC file address given on the page in the Cloud Security Gateway portal. For Private Access standalone users, endpoint should use the PAC file address given on the page. Check that the PAC file has entries for the Service edge address associated with your hosting site. If the PAC file does not contain the correct entries:
Using a tool such as Domain Information Groper (dig) or cURL, make a request to the service edge address to ensure it can be resolved to an IP address. Using Chrome Developer Tools or similar, generate a .HAR (HTTP Archive) file for your request to the private application, to check that the request is being routed to the correct location. This file can also be provided to Forcepoint support to assist with troubleshooting. |
| Certificate error | A certificate error such as "Your connection is not private" or "This site's security certificate is not trusted" can be displayed if the connection is HTTPS and the user does not have the Forcepoint root certificate installed. |
Check that you have installed the Forcepoint root certificate on your test machine.
|