Policy Server, Filtering Service, and State Server
If your deployment includes multiple instances of Filtering Service that might handle a request from the same user, an optional component, State Server, can be installed to enable proper application of time-based actions (Quota, Confirm) or overrides (Password Override, Account Override).
When State Server is installed, it allows its associated Filtering Service instances to share timing information, so users receive the correct allotment of quota, confirm, or override session time.
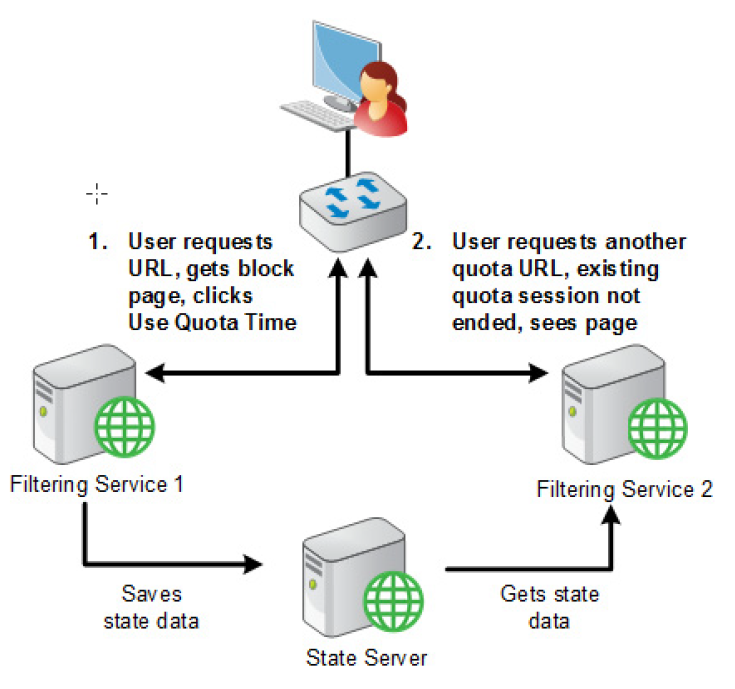
State Server is typically installed on a Policy Server machine, and only one State Server instance is required per logical deployment. A logical deployment is any group of Policy Server and Filtering Service instances that might handle requests from the same set of users.
- All Filtering Service instances that communicate with the same State Server instance must share the same time zone, and the time on all machines must be in synch.
- Each Filtering Service instance can communicate with only one State Server.
- All Filtering Service instances associated with the same Policy Server must communicate with the same State Server.
- Multiple Policy Server instances can share a single State Server.
Configure which State Server instance a Policy Server communicates with on the page in the Forcepoint Security Manager (see Configuring filtering settings).
In a geographically dispersed organization, where each location has its own Policy Server and Filtering Service instances, deploy one State Server instance (on the Policy Server machine or appliance) at each location. For example:
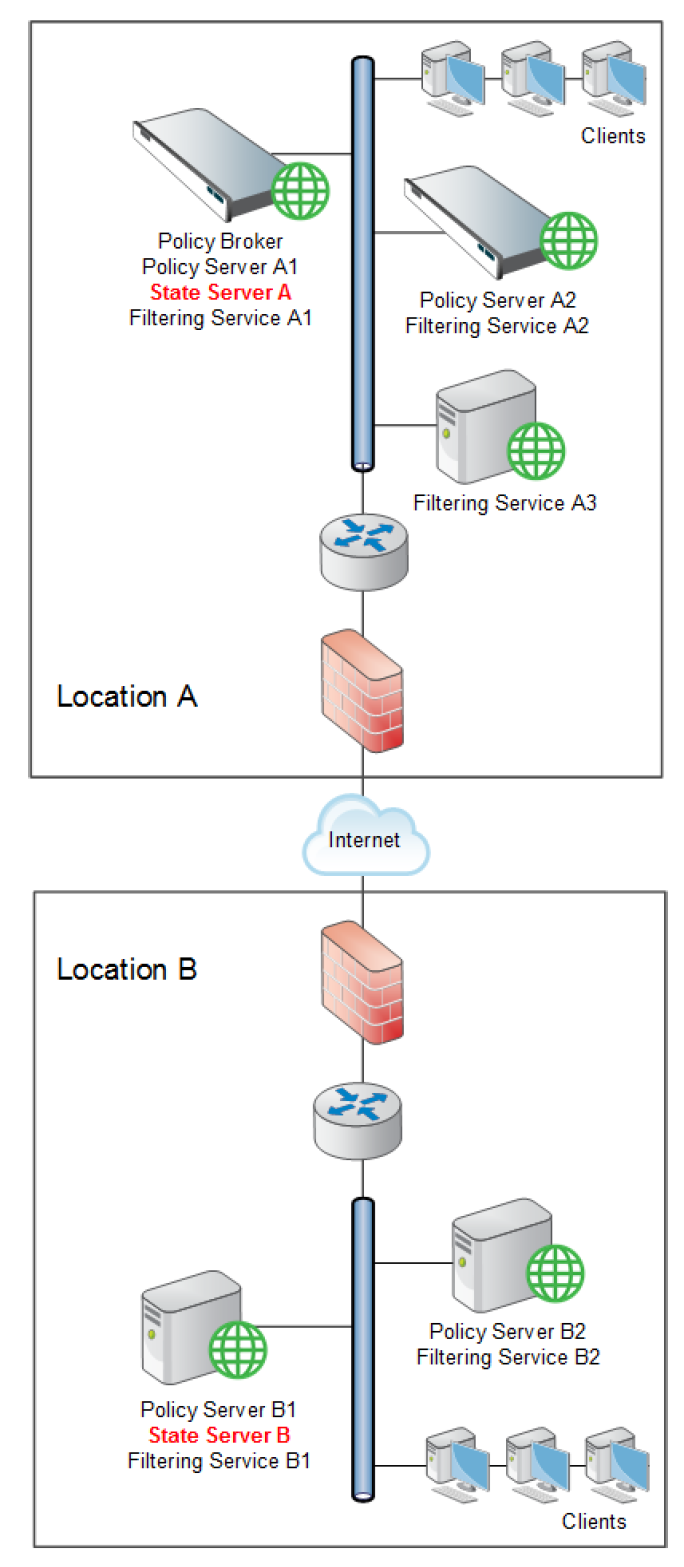
In an organization where all requests are managed through a central location, only one State Server instance is needed.