Configure Zero Trust Network Access
Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE's Agentless and Agent-based Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) provides an alternative to VPNs allowing admins to provide inline protection to internal apps without the need for VPN service to be running on the user's local machine.
This solution works by installing a ZTNA connector on your network where your internal apps are hosted and users off network will be able to launch those apps via the Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE and be given controlled access to those apps. This guide page will walk you through installation and configuration.
What is ZTNA
ZTNA is a way to control access to your applications from a standpoint of denying access by default and only granting access to those allowed. While ZTNA itself is a concept that can be applied in numerous ways (Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE already provides ways to perform ZTNA type controls to cloud apps via our SAML proxy capabilities), this new feature introduces a way to perform the same level of restrictive access to your internal apps without the need for a VPN for users off network.
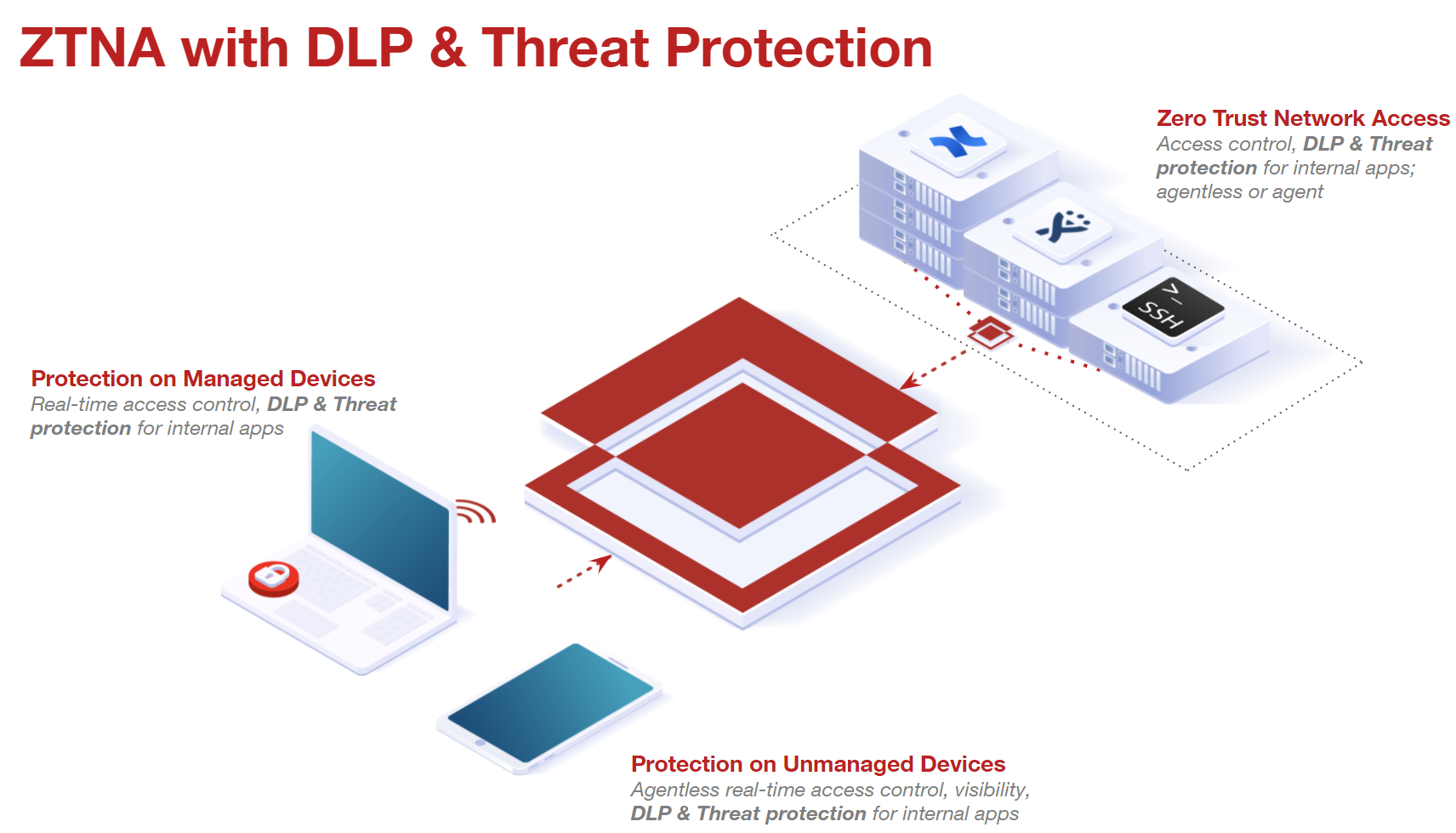
Customers controlling access to internal apps when users were remote were limited to relying on VPN functionality. While this method works - VPNing into your network would allow the user to access or use the app they needed while remote - also presents a couple of drawbacks. First, users over VPN will also have access to the entire network allowing them to access all apps and systems they would normally have access to while in the office. VPNs can also create network or bandwidth issues slowing users down if they are needing to VPN into a network far away from them (that is, user is on vacation and is in another state or country). Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE's agentless and agent-based ZTNA instead allows admins to specifically grant access based on contextual variables (such as the user/group, device type/OS, managed vs unmanaged devices, location, and so on) to specific on-prem apps without the need for a VPN service on the device. This method will not disrupt the user's normal internet activity on their device and only tunnel/grant access to the specific app instead of the entire corporate network. In addition, this method will allow Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE to proxy the traffic to the application and apply inline DLP controls. So not only will admins be able to restrict access to internal apps at a very granular level, but admins will also be able to apply inline controls preventing possible data leakage attempts or malicious uploads/downloads.
The way this works is by installing SmartEdge Agent on the user's machine and installing a connector within user's network environment. Once installed, you can then add which internal apps will be controlled by this connector. Users will launch apps through the Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE that they are given access to (sent to the ZTNA connector) which will then redirect them through the Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE ZTNA servers to proxy their traffic.
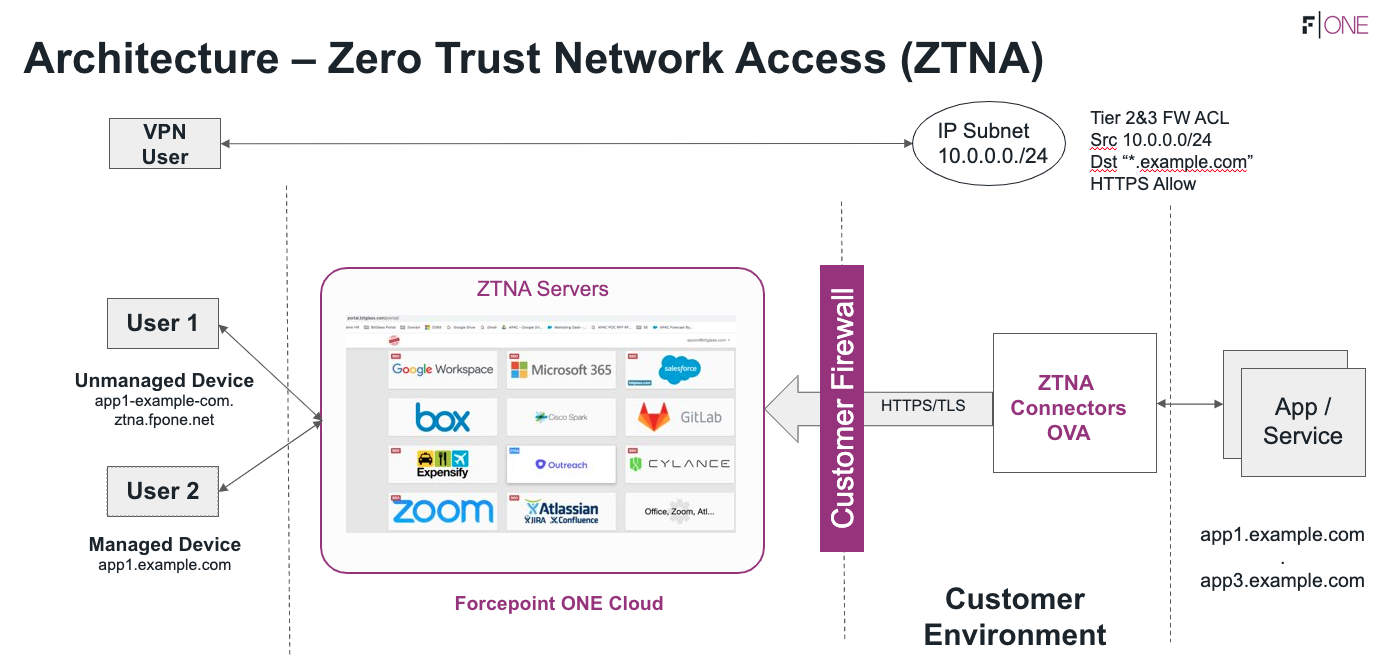
The only difference between agentless ZTNA and agent-based ZTNA is that for agent-based ZTNA, SmartEdge Agent 1.6.1 or newer needs to be installed on the end-user's machine and the end-user's machine should have Windows 10 or newer OS.