Generating Web debug logs
Steps to generate web debug logs.
Steps
-
Click the Debug button to begin debugging and to gather Web debug logs.

Once you click the Debug button, the Debug button disappears and the Debug Mode Pending message appears briefly until the logs start showing up.

- Generate web traffic.
-
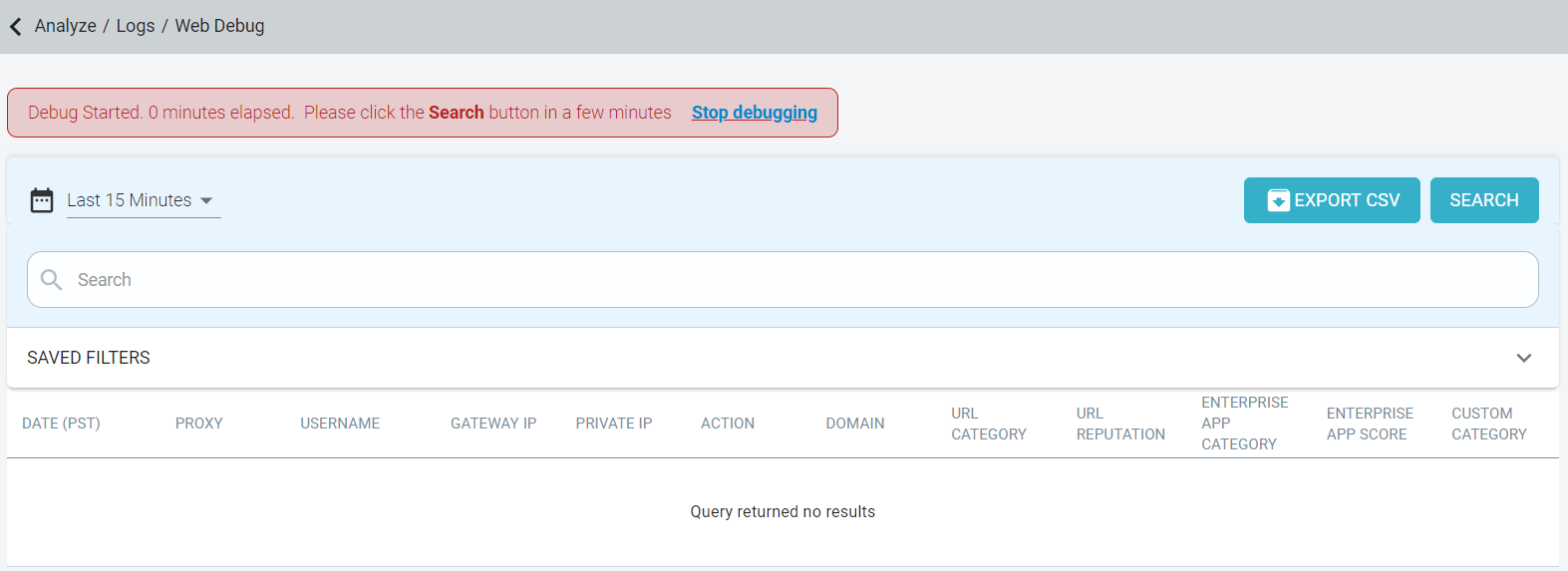
On the top of the page, an alert with the Debug started. # minutes elapsed. Please click Search button in a few minutes is displayed. The exact elapsed time in
minutes is displayed so that you are not confused when to click the Search button. The debug logs will be displayed preferably within 5 minutes.
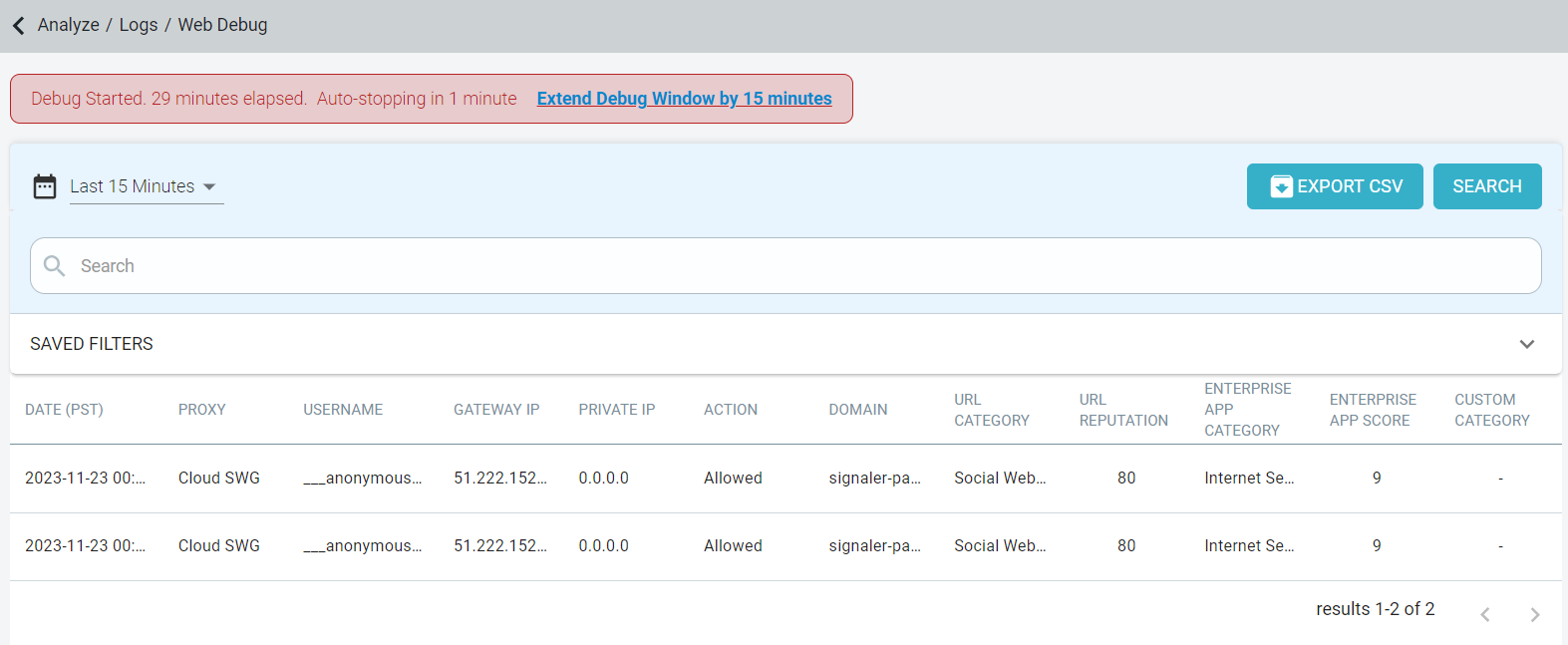
Debug window lasts 15 minutes long. When you are close to the 15 minute timer, you will be warned that you are approaching the 15 minute end of debug window and an option to extend the debug window by 15 minutes.
-
Click the Extend Debug Window by 15 minutes link to extend the debug window by additional 15 minutes.
OR
Wait for debug window to end automatically.
-
From the Time filter drop-down, select the time period for which you want view the debug logs.
Available options are:
- Last 15 Minutes (default)
- Last 30 Minutes
- Last 1 Hour
- Custom
When you select Custom, you should select Start Time and End Time to view logs for selected period. You can view logs for a maximum period of last 30 days from today.

The Web Debug logs page displays 50 entries per page and latest 5000 entries in total.
-
In the Search field, configure and filter the logs by any of the columns displayed. See below for information on each of these columns.
-
Proxy: Displays the proxy that generated the log.
- Can be filtered by equals or not equals and then select Agent or Cloud SWG option.
-
Username: Displays the user's Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE username.
- Can be filtered by equals, not equals, contains or does not contain and then entering characters or the username.
-
Gateway IP: Displays the public IP address of the site that the user was using for the event.
- Can be filtered by equals, not equals, contains or does not contain and then entering the IP or numbers.
-
Private IP: Displays the private IP address of the datacenter that the user was using for the event.
- Can be filtered by equals, not equals, contains or does not contain and then entering the IP or numbers.
-
Action:Displays the action taken by Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE.
- Can be filtered by equals or not equals and then select the one of the option (Alert, Allowed, Authenticate, Denied, Notify, Process via Cloud and Isolated).
-
Domain:Displays the website's domain URL that was being accessed.
- Can be filtered by equals, not equals, contains, does not contain, start with or ends with and then entering characters
-
Web Browsing Category or URL Category:
- The Web Browsing Category column is available when the ThreatSeeker URL Categories feature is disabled. The Web Browsing Category column displays the category the site falls into from Webroot.
- The URL Category column is available when the ThreatSeeker URL Categories feature is enabled. The URL Category column displays the category the site falls into from ThreatSeeker URL Categories.
Can be filtered by has or does not have and then selecting the category from the list.
-
Web Reputation or URL Reputation:
- The Web Reputation column is available when the ThreatSeeker URL Categories feature is disabled. The Web Reputation
column displays the sites Web Reputation score on a scale of 0-100 from Webroot.
- Can equal or not equal different reputation ranges - Trustworthy (81-100), Low Risk (61-80), Moderate Risk (41-60), Suspicious Risk (21-40), High Risk (1-20).
- The URL Reputation column is available when the ThreatSeeker URL Categories feature is enabled. The URL Reputation
column displays the sites "URL Reputation" score on a scale of 0-100 from ThreatSeeker URL Reputation.
- Can equal or not equal different reputation ranges - Very Safe (90-100), Fairly Safe (80-89), Marginally Safe (70-79), Suspicious (60-69), Harmful (0-59)
- The Web Reputation column is available when the ThreatSeeker URL Categories feature is disabled. The Web Reputation
column displays the sites Web Reputation score on a scale of 0-100 from Webroot.
-
Enterprise App Category: Displays the category the site falls into from Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE's category list.
- Can be filtered by has or does not have and then selecting the category from the list.
-
Enterprise App Score: Displays the sites app score on a scale of 0-10 based on Forcepoint Data Security Cloud | SSE's scoring.
- Can equal or not equal different reputation ranges - Trustworthy (9-10), Low Risk (7-8), Moderate Risk (4-6), Suspicious Risk (2-3), High Risk (0-1).
-
Custom Category: Displays the custom category object that admins may have configured on the Protect > Objects > > Common Objects page for controlling or allowing specific groups of sites.
- Can be filtered by has or does not have and then selecting the category from the list.
You can create and save filters as needed. For example, creating a filter where Proxy equals Cloud SWG and URL Category equals Social Web - YouTube.

-
Proxy: Displays the proxy that generated the log.
- If required, click Export CSV to export filtered logs in a zipped csv file. The CSV file contains latest 25000 records with all the fields.
-
Click on the log line to view the Web Debug Transaction Details page.
The Web Debug Transaction Details provides further information about the event including information such as the HTTPs request transaction being made (method type), bytes being sent/received, further information about the user's device (that is, hostname), as well as more detailed information drawn from our cloud app repository of the app or site being accessed.
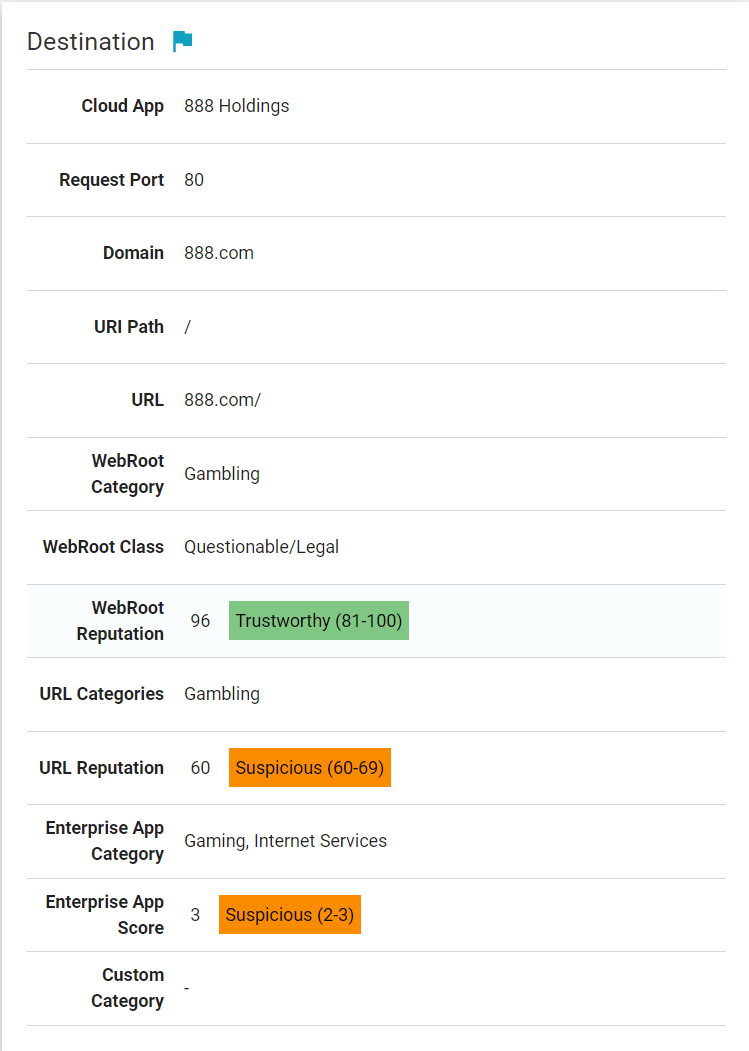
The following is an example of the Web Debug Transaction Details page when the ThreatSeeker URL Categories feature is disabled:

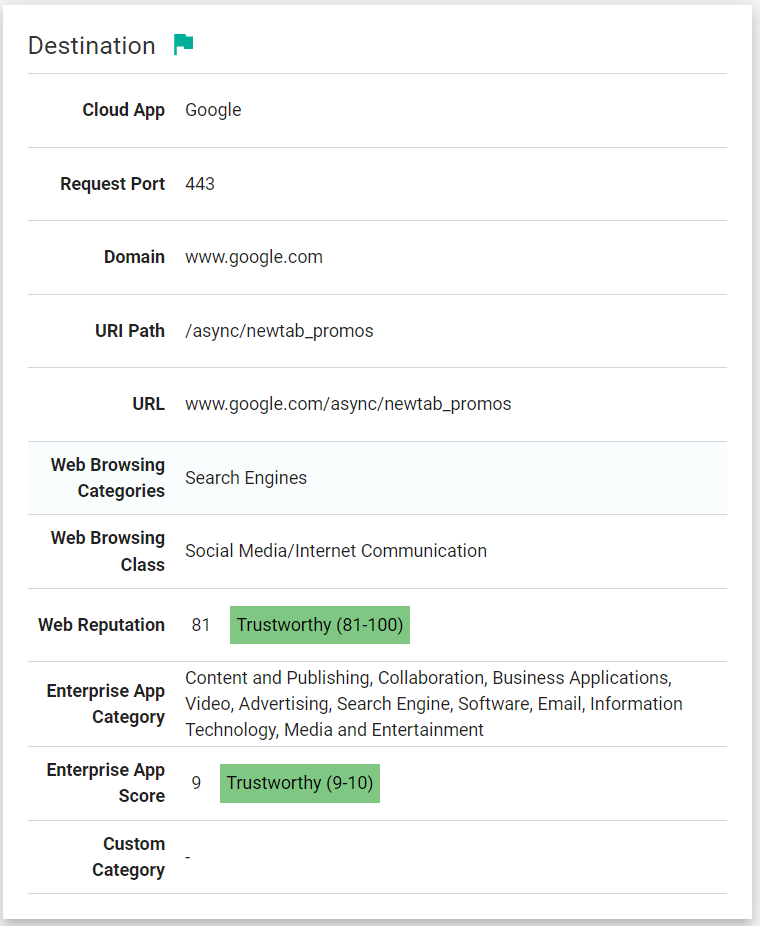
The following is an example of the Web Debug Transaction Details page when the ThreatSeeker URL Categories feature is enabled: